Two geospatial technology companies, Rezatec and Seequent, The Bentley Subsurface Company, have unveiled significant updates to their platforms, aimed at tackling the increasingly complex challenges in dam safety and civil infrastructure projects. Combining advanced AI, satellite data, and 3D subsurface modelling, both companies are setting a new benchmark for safety and productivity across critical infrastructure sectors.
Rezatec’s new Dam Monitoring geospatial AI platform
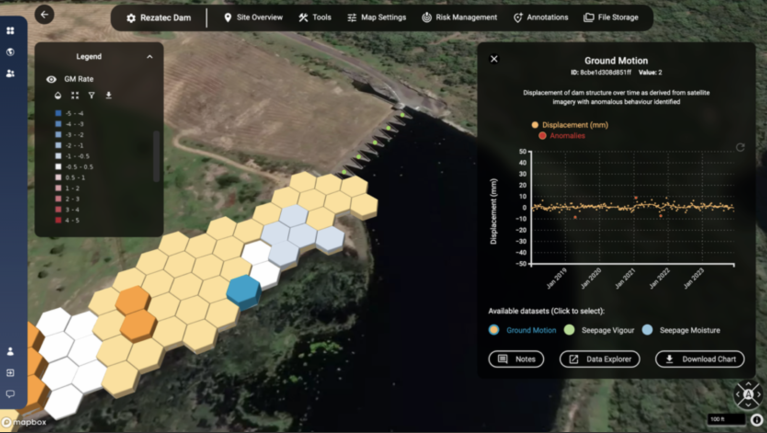
In September, Rezatec announced the launch of its enhanced Dam Monitoring solution, powered by its new geospatial AI platform. The new Dam Monitoring release enables centralized dam record management by digitizing and storing all dam information in one place and enhances it with satellite data and analysis for tracking unusual changes in ground movement, seepage, vegetation and downstream hazards.
Featuring the most advanced AI and visualization engine on the market, the solution analyses data and highlights potential issues on, around and downstream of the dam structure. This underpins potential failure mode monitoring and provides a unique risk management tool that drives existing dam and reservoir safety to the next level, the company said.
“As dam operators and regulators seek to improve their risk-informed decision making, it’s vital that they consider every aspect of data to identify and prioritize risks and develop mitigation measures,” said Camilla Braithwaite, Head of Product at Rezatec. “This new Dam Monitoring solution, powered by Rezatec’s geospatial AI platform, leverages the most comprehensive and robust data sets combined with world-leading AI models and visualizations, to help dam operators and regulators determine, assess and dynamically manage exact risk areas on and around the dam.”
The new Dam Monitoring release combines four core modules:
*Compliance: Creates a centralized dam record by digitizing and storing all dam information in one place and applies powerful analytics and visualization to all rainfall measurement, instrumentation, water level, geo technical and level survey data. Enables easy dam record management and regulatory reporting.
*Ground Motion & Seepage: Uses satellite data and AI to remotely determine unusual changes in ground movement, seepage and vegetation mapped onto the structure. Year-round monitoring across the entire dam fills data gaps between manual inspections or in between sensor sites, and millimetric change alerts provide early warning on potential issues. Combines with dam record data to boost risk informed decision making and enable targeted ground resources.
*Downstream Hazard: Identifies the building changes in dam flood zones that have the potential to change hazard ratings across entire dam portfolios state-wide. Reduces the manual burden involved in collecting this information, enables targeted risk identification and supports emergency action planning.
*Risk Management: A unique risk matrix represents likelihood and consequence of failure metrics for each of the potential failure modes for a dam. Enables dynamic, comprehensive risk management.
Dam Monitoring customer Daniel Turnbull, Dam Safety Engineer, Hunter Water commented: “Rezatec are continuously improving this solution, and I’m impressed with these latest enhancements which are driving us in the way we use data and what to focus on. At Hunter Water we are confident we are doing everything in our power to exceed regulatory requirements and safeguard our dams and the surrounding population.”
“Rezatec’s new geospatial AI platform puts complex data science into the hands of dam operators and regulators by efficiently processing terabytes of satellite and unstructured data and featuring additional new tools including change alerts, 3D mapping, cluster analysis, benchmarking and reporting. Its powerful insights are easy to access and straightforward to use, providing a systematic catalyst for assessing the safety of dams, reservoirs and levees,” added Braithwaite.
Seequent’s Leapfrog: 3D geological modelling for complex projects
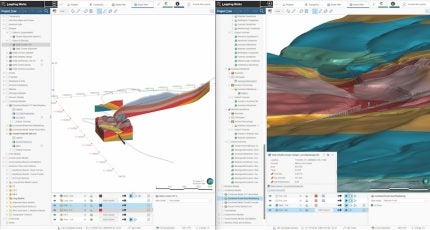
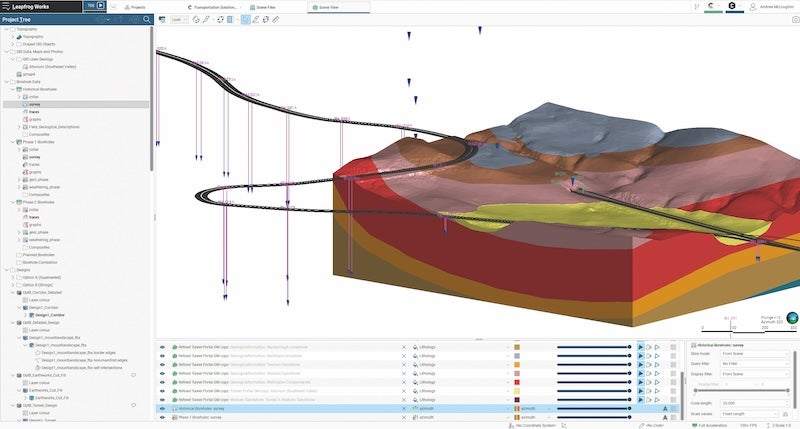
Meanwhile, Seequent, the Bentley Subsurface Company, has unveiled a considerable update to its 3D earth modelling and analysis tool Leapfrog. The new functionality enhances core tools and workflows to improve productivity and help solve a range of geoscience challenges in civil infrastructure and environmental projects.
Highlights for Leapfrog Works include:
- Ability to run multiple instances of Leapfrog on a single machine for project multi-tasking
- Visualisation of downhole survey data to aid drilling analysis
- Attributed mapping data to create better models more quickly
Rachel Murtagh, Product Manager, Geology, Geostatistics and Data Science, Seequent, said: “The industries we serve are solving critical challenges under increasingly tighter economic and ESG (Environmental, Social and Governance) conditions. Our goal is to help our customers focus as much of their time as possible on the geoscience. The latest update of Leapfrog emphasises enhanced productivity, investment in core functionality and puts in place key capabilities to enable an evolving future.”
Leapfrog’s continued customer-led evolution resonates with users and is demonstrated in the number of models created with our software, added Murtagh.
In 2023, Leapfrog users created nearly 200,000 new geological models, providing crucial subsurface insights for mining, civil, energy, and environmental projects.
“We spend a lot of time listening to customers about what they need to succeed, and we iteratively work through a discover-design-build-test loop with expert and early user groups. This ensures we capture the feel and function that works best of our customers allowing them to master new workflows quickly and become experts in dynamic modelling so they can better understand the subsurface and its resources.
“Leapfrog 2024.1 is a strong release that strengthens and broadens key capabilities of Leapfrog and significantly enhances the users’ experience.”
Enabling the future of geoscience
3D subsurface modelling software Leapfrog Works for civil engineering and environmental projects allows users to build and refine models fast.
“Seequent pioneered implicit modelling in geology with Leapfrog, and we’re still leading the way. Its user-centric, intuitive, well-designed interface and dynamically linked workflows hugely simplify the updating of models with new data. So, we are continuing to build on what’s made Leapfrog so successful,” said Murtagh.
Leapfrog 2024.1 release updates boost 3D modelling, interoperability, and visualisation capabilities:
- Users can now run multiple instances of Leapfrog on a single machine, whilst utilising a single seat. This allows users to work faster, working on one project while another one runs simultaneously.
- Drilling improvements deliver new visualisation and access to survey data. The visualisation of downhole survey data provides additional insights and validation of drill hole orientation to aid drilling data analysis. Features to evaluate and sub-set by geology, drilling orientation, drilling type, hole diameter and more are also enabled. Other drilling improvements focus on saving time when modelling resource grade or contaminants, flexible tools to execute complete workflows, and gaining more comprehensive context for data in the 3D context alongside other geological information.
- Improvements to geological modelling with new flexibility for inputs help users create better informed models quicker by supporting attribution of mapped data, improve insights into the data points influencing the model surfaces with updates to mesh surface values, and provide better control over vein surfaces when modelling.
With an eye to the future, the Leapfrog 2024.1 release also includes technologies to improve interoperability between desktop and cloud products, which, in the future, will unlock hybrid workflow opportunities through the new geoscience data platform being built by Seequent.
As industries face increasing economic, environmental, and safety pressures, tools like Rezatec’s Dam Monitoring and Seequent’s Leapfrog are enabling professionals to make data-driven decisions with unprecedented precision. These innovations represent a leap forward in how geoscience, engineering, and environmental sectors approach complex challenges.






